How do portable power stations work
Overview of Portable Power Stations
Portable power stations are compact, rechargeable battery systems that store and provide electrical energy for various devices and applications. They have multiple output ports, allowing users to charge and power gadgets such as smartphones, laptops, cameras, and small appliances. These versatile devices are ideal for outdoor activities like camping, hiking and emergencies when traditional power sources are unavailable.
Importance of Understanding the Technology
Understanding the technology behind portable power stations is crucial for several reasons:
- Informed Decision-Making: Knowledge of different components—such as battery types, inverters, and charging mechanisms—helps consumers select the right power station based on their specific needs and usage scenarios.
- Optimal Usage: Familiarity with how portable power stations operate allows users to maximize their performance, ensuring efficient energy management and prolonging battery life.
- Safety Awareness: Awareness of safety features and potential risks associated with the technology can help users operate these devices safely, reducing the chances of accidents or equipment damage.
- Sustainability Considerations: Understanding the impact of different battery technologies can guide users toward more environmentally friendly choices, especially as renewable energy options, like solar charging, become increasingly popular.
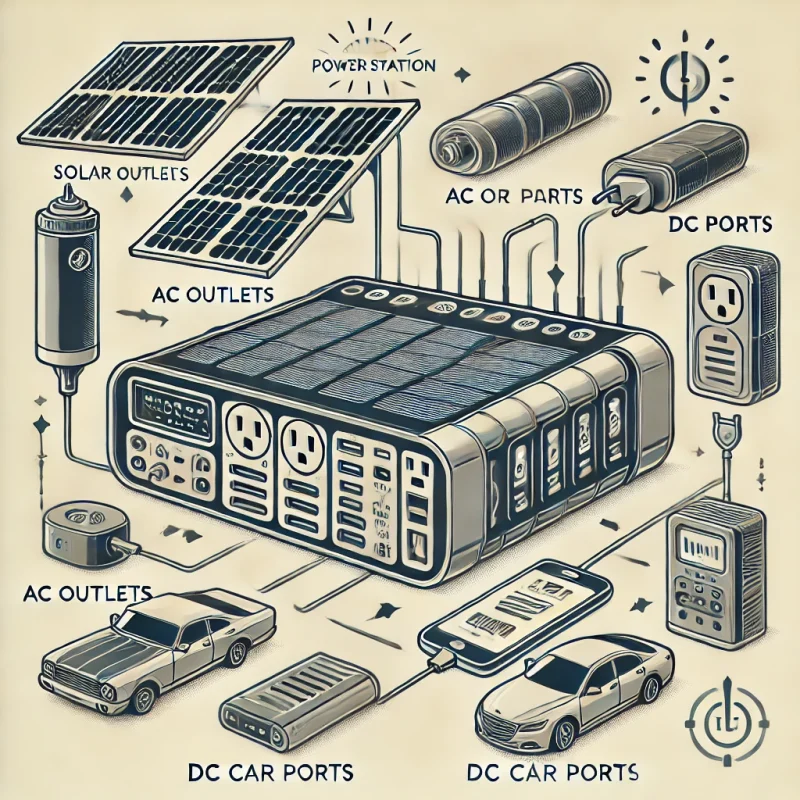
Critical Components of Portable Power Stations
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| A. Battery | – Types: Lithium-ion, lead-acid. – Role: Stores energy and affects overall performance. |
| B. Inverter | – Function: Converts DC (direct current) from the battery into AC (alternating current). – Importance: Essential for powering standard household devices. |
| C. Charge Controller | – Explanation: Manages the charging process, ensuring safe and efficient charging. – Protection: Prevents overcharging and excessive discharging of the battery. |
| D. Input Ports | – Description: Includes various charging ports (AC, USB, DC). – Purpose: Facilitates the connection of power sources and devices. |
| E. Output Ports | – Types: Multiple output options are available for different devices. – Ability: Can power several devices simultaneously. |
| F. Display Panel | – Overview: Shows real-time information about battery status, output, and input levels. – Importance: Helps users monitor power usage and remaining capacity. |
| G. Cooling System | – Explanation: Ensures efficient operation by dissipating heat generated during use. – Importance: Critical for maintaining performance and safety. |
| H. Solar Input (if applicable) | – Overview: Some models can be charged using solar panels. – Benefits: Provides a sustainable and eco-friendly power source. |
Applications and Use Cases
| Application/Use Case | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Camping | Provides power for lighting, cooking, and charging devices outdoors. | Reliable electricity access in remote locations. |
| Emergency Situations | Keeps essential devices operational during power outages. | Ensures safety and connectivity in critical times. |
| Off-Grid Living | Supplies energy for appliances and devices in remote areas. | Sustainable energy source without grid reliance. |
| Outdoor Events | Powers sound systems, lighting, and equipment at festivals and gatherings. | Enhances overall experience and convenience. |
| RV and Van Life | Enables the use of appliances and electronics while traveling. | Comfort and convenience on the road. |
| Construction Sites | Provides power for tools, equipment, and lighting in areas without electrical outlets. | Facilitates work efficiency and productivity. |
| Tailgating and Picnics | Powers portable grills, coolers, and entertainment devices at social gatherings. | Adds convenience and fun to outdoor events. |
| Remote Work | Keeps laptops and equipment running in non-traditional locations. | Provides flexibility and productivity in work settings. |

Common Application, power requirements, and plug
| Application | Power Requirements | Plug Types |
|---|---|---|
| Camping | Varies (up to 500W for small appliances) | AC outlets, USB ports |
| Emergency Backup | Essential devices (100-1000W) | AC outlets, USB ports |
| Outdoor Events | Moderate power (up to 1000W) | AC outlets, DC ports |
| RV and Van Life | Higher power (500-2000W for appliances) | AC outlets, DC ports |
| Construction Sites | Tools and equipment (up to 1500W) | AC outlets, DC ports |
| Hiking and Tailgating | Low to moderate (100-500W) | USB ports, AC outlets |
| Remote Work | Moderate (up to 500W for laptops) | AC outlets, USB ports |
| Home Use | Small appliances (up to 1000W) | AC outlets, USB ports |
Conclusion
- Recap of how portable power stations work.
- Encouragement to consider specific needs when selecting a power station.







